Top Tips For Using CBD For Arthritis Pain Management
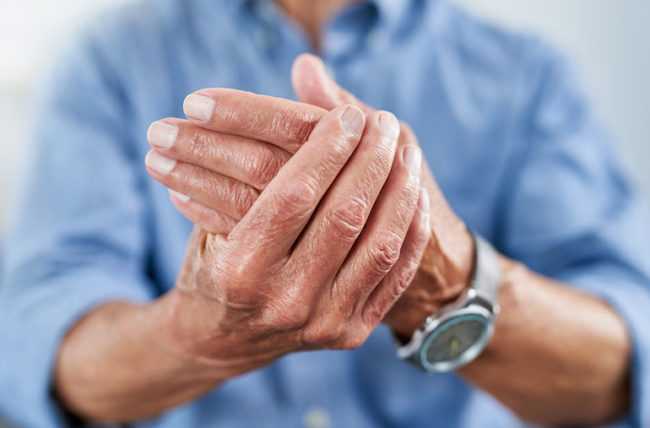
HCN– Cannabidiol (CBD) has been widely popularized as a potential treatment for forms of chronic pain such as arthritis pain and other types of joint pain. Does the science support the idea that CBD might be useful for pain and inflammation, and if so, which types of CBD products are best for rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and other arthritic conditions?
Does CBD help with arthritis?
First, let’s observe the anecdotal evidence. Treating arthritis pain is one of the most commonly cited CBD uses among people who are taking CBD regularly. According to a recent survey conducted by the Arthritis Foundation, 29% of people with arthritis report that they currently use CBD. Even more impressively, close to 80% of survey participants reported that they had used CBD in the past or planned on using CBD oil to treat their arthritis soon.
Arthritis sufferers who have experienced positive results after using CBD have recommended their favorite CBD products to their friends, and the popularity of CBD use within the arthritis community has snowballed within the United States and beyond. While the FDA has not yet approved any CBD-based drugs as arthritis treatments or classified this substance as a supplement viable for arthritis pain, clinical trials are underway to determine the potential pain relief benefits that CBD may provide to arthritis patients.
What studies say about CBD and arthritis.
Initial research into the benefits of CBD and arthritis has been highly promising. As we examine the animal studies and other forms of research that have been conducted into the potential benefits of CBD for arthritis pain, we’ll begin with an exploration of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and its potential involvement in arthritic pain. According to cannabis scientists, the ECS is a complex regulatory system that controls bodily processes as wide-ranging as mood, metabolism, and cardiovascular functioning.

(John Carey/Unsplash)
Most relevant to our current topic, however, is the fact that recent research indicates that the ECS may modulate pain related to osteoarthritis. Since this complex regulatory system is also believed to modulate most types of pain caused by inflammation, it’s possible that stimulating the ECS may deliver pain relief to individuals suffering from other types of arthritis as well.
CBD has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory properties
CBD is believed to gently stimulate the ECS. The cannabis plant contains many different cannabinoids, and the THC/CBD divide is very wide when it comes to each cannabinoid’s effects. While recreational or medical marijuana containing high concentrations of THC might relieve pain under certain circumstances, this derivative of the cannabis plant is intoxicating and causes side effects like paranoia and anxiety, and THC also has considerable habit-forming properties.
CBD, on the other hand, is non-intoxicating, non-addictive, and free of serious side effects. Like THC, CBD has been examined for its potential pain-relieving properties, and research into CBD for pain and inflammation has delivered promising results so far.
In 2020, for instance, researchers re-examined the available evidence on CBD and inflammation, and they found that “CBD seems to be more preferred than other compounds from the phytocannabinoid group.” This means that CBD is preferable to other cannabinoids when it comes to relief from inflammation. The researchers who conducted this study also found that CBD improves the safety profile of THC when these two cannabinoids are ingested together.
CBD may interact with the nervous system’s TRPV1 receptors and cause various symptoms.
(Images: Verywell Health)
If it’s true that CBD has anti-inflammatory properties, how, exactly, do CBD products exert these effects? As researchers investigated the chemical properties of CBD, they discovered that this cannabinoid does not significantly stimulate the conventional cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2. Instead, CBD actually acts as an agonist at the cB1 receptor, making it more difficult for this receptor to bond with THC.
Rather than interacting with the CB1 or CB2 receptors, CBD appears to primarily interact with the 5-HT1A and TRPV1 receptors, which are neuroreceptors that are involved in the modulation of chronic pain. While activating your 5-HT1A receptors provides relief from neuropathic pain, activating your TRPV1 receptors provides relief from inflammatory pain, which is the primary type of pain involved in arthritis.
Scientists have affirmatively linked TRPV1 activation to arthritis pain relief, and recent research confirms that CBD appears to activate your TRPV1 receptors. If true, TRPV1 activation may explain why so many people have experienced relief from rheumatoid arthritis pain and other types of arthritic pain by using CBD oil and topical CBD.
CBD does not appear to have any significant side effects
At this point, people who want to use CBD for arthritic pain might be feeling like this is all too good to be true. There must be at least one reason not to use a high-quality CBD product for arthritis pain and other types of joint pain, right?
The truth is that, despite extensive research, scientists have not been able to determine any significant side effects of CBD. This cannabinoid can very rarely cause intense adverse reactions in particular individuals, and CBD can also cause serious drug interactions. Used on its own, however, CBD has an impressive safety profile.
Research indicates that CBD is tolerable in concentrations exceeding 1500mg, and this cannabinoid has very low toxicity whether used orally in the form of CBD oil or topically in the form of a lotion or a salve. At the same time, it’s also been determined that even a low dose of CBD provides impressive effects.
How to use CBD for arthritis symptoms
So far, no official agencies have released usage guidelines for CBD, and it’s not our place to provide medical advice. We can, however, offer a basic overview of the types of hemp-derived CBD products that are available and help you choose the right product type for your needs.
CBD topicals vs. CBD oils
Since they deliver CBD directly to the site of your joint pain, you might find that topical CBD products provide more profound relief in specific areas. If you want to experience widespread effects, however, taking CBD in the form of ingestible CBD oil might be a better choice.
How often should people with arthritis take CBD?
You can enjoy the benefits of CBD as much as you’d like throughout the day since this cannabinoid doesn’t pose any significant dangers to your health.
How to choose the best CBD products for arthritis
As you pick the right CBD product for your arthritic pain, keep in mind that the 2018 Farm Bill stipulates that any CBD products containing more than 0.3% THC are medical cannabis, not industrial hemp. As a result, it’s important to check if a CBD product you’re considering comes with a certificate of analysis proving that it contains less than 0.3% THC.




































